Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to develop a PL/SQL function and how to call it in various places such as an assignment statement, a Boolean expression, and an SQL statement.
Similar to a procedure, a PL/SQL function is a reusable program unit stored as a schema object in the Oracle Database. The following illustrates the syntax for creating a function:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name (parameter_list) RETURN return_type IS [declarative section] BEGIN [executable section] [EXCEPTION] [exception-handling section] END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)A function consists of a header and body.
The function header has the function name and a RETURN clause that specifies the datatype of the returned value. Each parameter of the function can be either in the IN , OUT , or INOUT mode. For more information on the parameter mode, check it out the PL/SQL procedure tutorial
The function body is the same as the procedure body which has three sections: declarative section, executable section, and exception-handling section.
In these three sections, only the executable section is required, the others are optional.
The following example creates a function that calculates total sales by year.
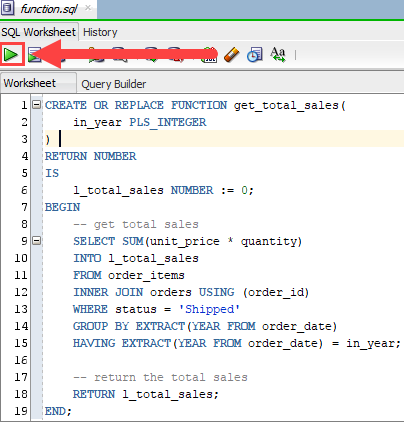
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_total_sales( in_year PLS_INTEGER ) RETURN NUMBER IS l_total_sales NUMBER := 0; BEGIN -- get total sales SELECT SUM(unit_price * quantity) INTO l_total_sales FROM order_items INNER JOIN orders USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' GROUP BY EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) HAVING EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = in_year; -- return the total sales RETURN l_total_sales; END;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)To compile the function in Oracle SQL Developer, you click the Run Statement button as shown in the picture below:

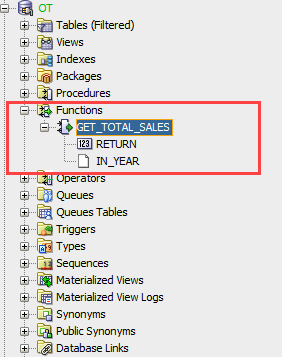
Once the function is compiled successfully, you can find it under the Functions node:
You use a function anywhere that you use an expression of the same type. You can call a function in various places such as:
1) in an assignment statement:
DECLARE l_sales_2017 NUMBER := 0; BEGIN l_sales_2017 := get_total_sales (2017); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Sales 2017: ' || l_sales_2017); END; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)2) in a Boolean expression
BEGIN IF get_total_sales (2017) > 10000000 THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Sales 2017 is above target'); END IF; END; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)3) in an SQL statement
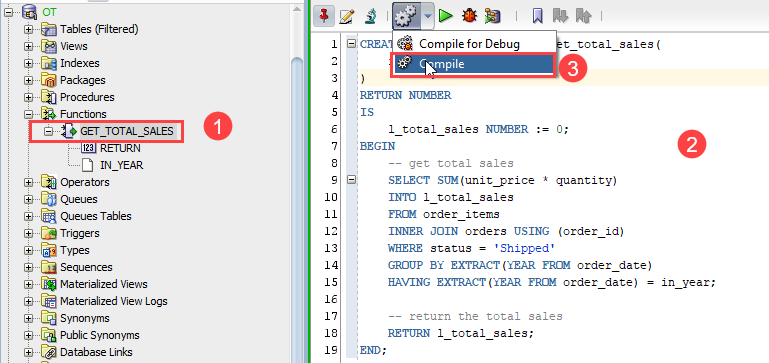
SELECT get_total_sales(2017) FROM dual; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)To edit and recompile an existing function, you follow these steps:
The DROP FUNCTION deletes a function from the Oracle Database. The syntax for removing a function is straightforward:
DROP FUNCTION function_name; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Followed by the DROP FUNCTION keywords is the function name that you want to drop.
For example, the following statement drops the GET_TOTAL_SALES function:
DROP FUNCTION get_total_sales; Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Oracle issued a message indicating that the function GET_TOTAL_SALES has been dropped:
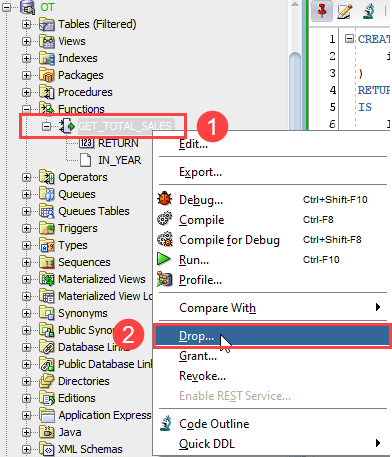
Function GET_TOTAL_SALES dropped. Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)If you want to drop a function using the SQL Developer, you can use these steps:
Now, you should know how to develop a PL/SQL function and call it in your program.